There are many Occupational Hazards in the work areas and these Hazards have been affecting the health and safety of the person. It can either lead to some of the chronic disease which sometimes may be irreversible or sometimes it may lead to a major injury which may make a person disabled for life. And in both cases the life of the person, his/her family or nearby of the person are affected no just physically, but mentally, emotionally and economically as well.
What is Occupational Hazard?
In layman’s terms, Occupational Hazard is something which has a potential to harm at work or during the job.
According to OHSAS, 18001:1999, Occupational hazard is a source or situation at workplace with a potential for harm in terms of human injury or illness, damage to property, damage to the environment, or a combination of these.
How to identify Occupational Hazard?
Since Occupational Hazard may harm in terms of human injury or illness, damage the property and/or environment, it is very important for individuals to acknowledge the hazards which are there, not just by health, safety & environment (HSE) teams but as every employee as well and assist HSE team to make the workplace safe and healthy place to work at.
Hazards are essentially a problem/risk, and if one doesn’t acknowledge the problem/risk there will be no action towards solutions/risk mitigation.
To identify Occupational Hazards, we need to have different perspectives and we can also categorize Hazards according to these perspectives, in the following way –
- Obvious Hazard – perceptible by senses. Some of the examples can be – unguarded machines, building defects, faulty electrical equipment & others.
- Concealed Hazard – not perceptible by senses. Some of the examples can be – toxic vapors, high frequency noise, electricity & others.
- Developing Hazard – these develop over a period of time and can’t be recognized immediately. Some of the examples can be old tyre of lifting equipment, payload trucks, frayed steel cables & others.
- Temporary Hazard – these are not always present or may not also come in future, but, can be there for a limited period of time. Some of the examples can be machine overloading, defects in the machines & others.
Other way of categorizing hazard is based on the following –
- Mechanical
- Electrical
- Radiation
- Substances
- Fire and explosion
- Toxic release
- Natural calamities
Combining these and making the matrix we will be able to assist you take the control measures.
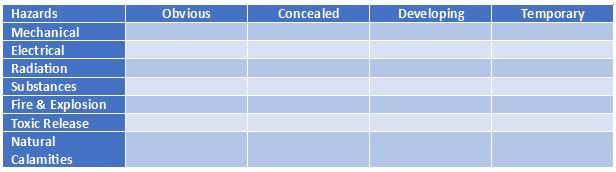
Once you have this matrix ready you can prioritize the control measures for each & every Hazards.
What are the general control measures to minimize the risks of Hazards?
- 1. Elimination – Best way to control the hazards is by eliminating the hazard.
- 2. Substitution – if a Hazard or work process cannot be completely eliminated, then try substitution, either for
process or the material which may cause Hazard. - 3. Engineering controls – these can be categorized into the following
- 4. Administrative controls – If the previous methods don’t work, administrative controls are used to limit the exposure the hazard by limiting the working hours for the workers in required work processes.
- 5. Personal Protective Equipment – These should be the last resort to fight the Hazards as use of PPEs may give produce other Hazards and sometimes may lead to worker’s inefficiency.
b. Isolation – move the work process where there is minimal density of workers to reduce the no. of workers exposed to Hazard.
c. Ventilation – helps to prevent environment to be extreme, and help the to diffuse the hazards in air.
Is creating the Hazard free environment for the workers and employees just the role of the employer and the management?
The management is continuously monitoring knows what are the Hazards at their workplace, they analyze the hazards and deploy the proper control measures. And this cycle continues.
But what if workers/employees are not following the instructions? The entire effort of deploying control measures goes down the hill an increase the risk of hazards for his/her colleagues as well. Hence it is very important for each and every employee and workers to work towards creating Hazard free work environment, and assist the work of HSE team to ensure your health & safety. This will also increase the efficiency of the workforce.
Can the stakeholders outside the organizations help? Yes definitely, they should also follow the instructions given to them while visiting the premises. Apart from that vendors who are providing raw material and machineries for the workplace should make sure that the raw materials be package in a good material to reduce the risk of exposure. Machineries should also be manufactured or assembled in such a way that it automatically isolates Hazards as far as possible. And it can also provide them with a competitive edge for this. In short the entire supply chain should be responsible for making the Workplaces across the Supply Chain Hazard free not the responsibility of individual entity to make workplace safe just for their own workplace.








